Distributed File System (DFS) is a powerful feature in Windows Server that allows you to group shared folders located on different servers into one or more logically structured namespaces. It also enables replication of folders across multiple servers for fault tolerance and load balancing. In this blog, we’ll walk you through the essential steps to configure DFS on your Windows Server environment.
Why Use DFS?
- Centralized Access: Users access files through a single namespace, regardless of where the files are physically stored.
- High Availability: DFS Replication keeps data synchronized across multiple servers.
- Load Balancing: Multiple folder targets improve performance and availability.
Step-by-Step Guide to Configure DFS
1. Install DFS Roles and Features
Start by installing the DFS roles on all servers that will participate.
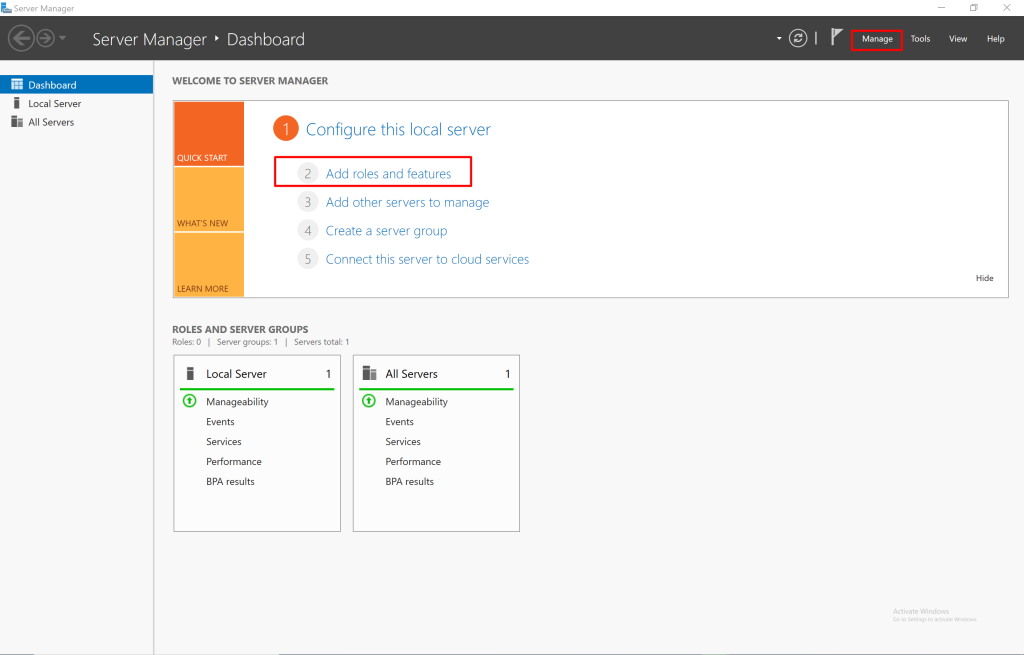
- Open Server Manager.
- Navigate to Manage > Add Roles and Features.
- Select DFS Namespaces and DFS Replication under File and Storage Services.
- Complete the installation.
2. Create a DFS Namespace
A namespace is a virtual view of shared folders.
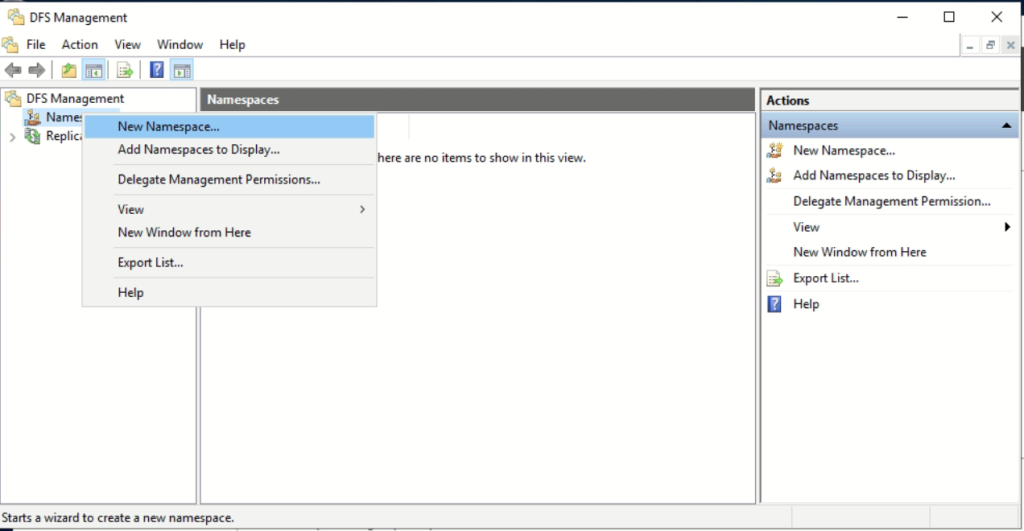
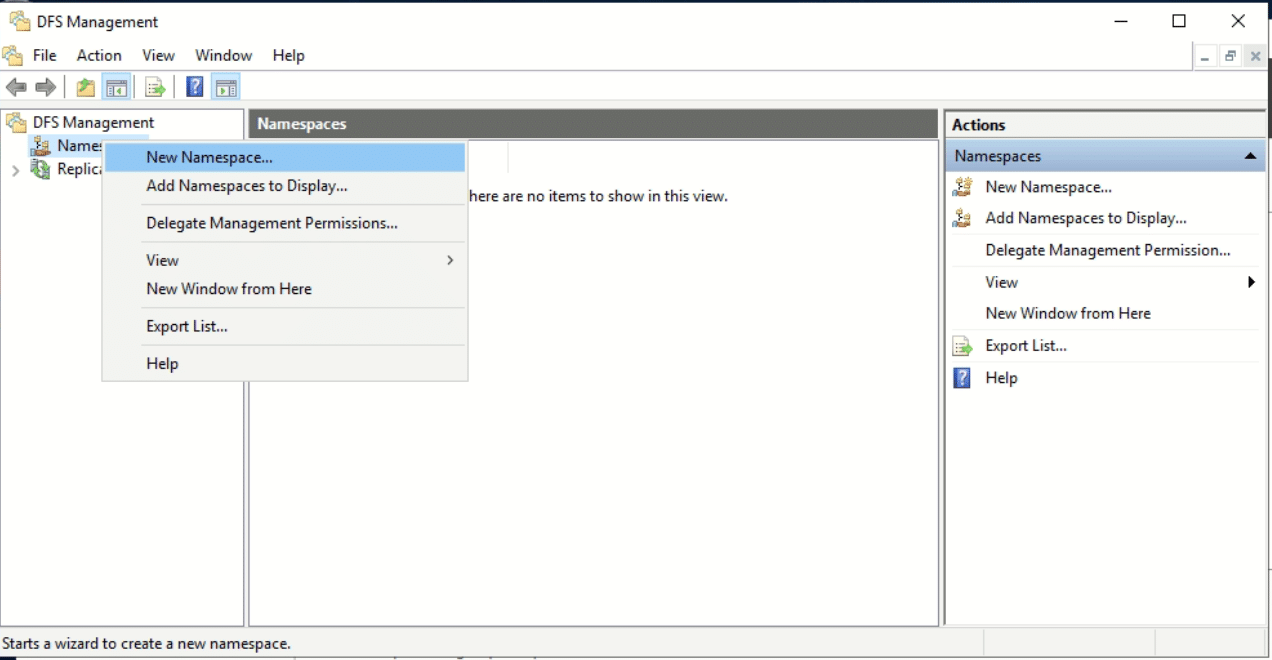
- Open DFS Management.
- Right-click Namespaces > New Namespace.
- Select the server to host the namespace.
- Name your namespace (e.g.,
\\domain.com\SharedFiles). - Choose Domain-based namespace for scalability.
- Set permissions and finish the wizard.
3. Add Folders to the Namespace
Add shared folders as targets within the namespace.
- Right-click your namespace > New Folder.
- Enter the folder name.
- Add folder targets by specifying shared folder paths on different servers.
- Click OK.
4. Configure DFS Replication
Replication keeps folder targets synchronized.
- In DFS Management, right-click Replication > New Replication Group.
- Choose Multipurpose replication group.
- Add member servers.
- Select folders to replicate.
- Configure replication topology and schedule.
- Finish the setup.
Configure Distributed File System (DFS) on Windows Server (F.A.Q)
Can DFS work across different domains?
DFS namespaces require servers to be in the same Active Directory domain or trusted domains.
What is the difference between standalone and domain-based namespaces?
Domain-based namespaces are stored in Active Directory and support fault tolerance; standalone namespaces are hosted on a single server without AD integration.
How often does DFS replication occur?
DFS replication is scheduled and can be configured to occur continuously or during specific time windows.
Can DFS handle file conflicts during replication?
Yes, DFS uses conflict resolution policies to handle file conflicts, typically keeping the latest version.