If you’ve ever tried to edit or save a file in Linux and got the dreaded “Read-only file system” error, don’t worry — you’re not alone. This error means that the filesystem has been mounted as read-only, preventing any modifications. It’s a common issue that can occur due to disk errors, improper shutdowns, or permission problems. In this post, we’ll walk through the main causes and how to fix them safely.
Common Causes
- Filesystem corruption: Power loss or improper shutdown can damage filesystem integrity.
- Hardware or disk errors: Bad sectors or failing drives may trigger a read-only mode.
- Improper mounting: The filesystem may have been mounted as read-only intentionally.
- Kernel panic or crash recovery: Linux automatically mounts drives as read-only to prevent data loss.
How to Fix the “Read-only File System” Error
1. Check Mount Status
First, confirm if the filesystem is mounted as read-only:
mount | grep 'on /'
If you see (ro) next to your mount point, it’s read-only.
2. Remount as Read-Write
You can try to remount it manually: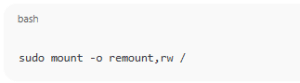
sudo mount -o remount,rw /
If successful, your filesystem should now allow write operations.
3. Check Filesystem Health
If remounting fails, check the disk for errors:
sudo fsck -Af -V
⚠️ Important: Run this command only when the disk is not mounted or from a live boot environment to prevent damage.
4. Reboot the System
Sometimes, a simple reboot can restore normal operation:
sudo reboot
5. Check Disk Health
If the problem persists, check for bad sectors: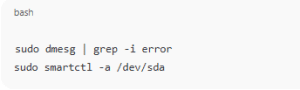
sudo dmesg | grep -i error
sudo smartctl -a /dev/sda
If SMART errors appear, consider backing up data immediately — your drive may be failing.
Preventive Tips
- Always shutdown or reboot properly.
- Use SMART monitoring to detect drive issues early.
- Keep regular backups of important data.
- Use journaling filesystems (like ext4) to minimize corruption risks.
Conclusion
The “Read-only file system” error in Linux usually points to a protective measure — your system is preventing damage. By remounting the drive, checking filesystem integrity, and ensuring hardware health, you can fix this issue effectively and avoid future disruptions.
How to Fix “Read-only File System” Error in Linux (F.A.Q)
Why does Linux make my filesystem read-only automatically?
Linux does this to protect data when it detects corruption or disk errors.
Can I fix the read-only error without rebooting?
Yes. You can try sudo mount -o remount,rw /, but if it fails, a reboot may be required.
Will fsck delete my data?
Not usually — it repairs filesystem structure, but always back up before running it.
What if my USB drive shows this error?
Unmount it, run fsck on the device (e.g., /dev/sdb1), and remount it as read-write.