Introduction:
Docker is a powerful platform for developing, shipping, and running applications. It allows you to containerize your applications, ensuring they run consistently across different environments. In this tutorial, we’ll walk you through the process of installing Docker on Ubuntu Linux.
Prerequisites:
Before you begin, ensure you have the following:
1. An Ubuntu Linux system (tested on Ubuntu 20.04 LTS).
2. Access to a terminal with sudo privileges.
Step 1: Update Package Lists
Before installing any new software, it’s a good practice to update your package lists to ensure you’re getting the latest versions. Open a terminal and run the following command:
sudo apt update
Step 2: Install Dependencies
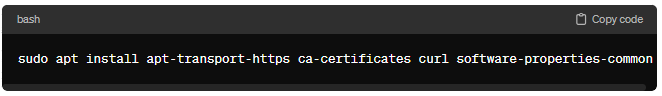
Docker requires some dependencies that need to be installed. Run the following command to install these dependencies:
sudo apt install apt-transport-https ca-certificates curl software-properties-common
Step 3: Add Docker’s GPG Key
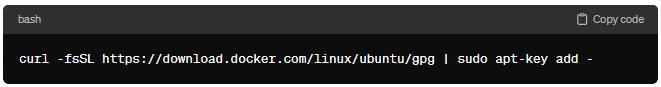
Next, add Docker’s official GPG key to ensure the integrity of the software packages you’re going to download:
curl -fsSL https://download.docker.com/linux/ubuntu/gpg | sudo apt-key add –
Step 4: Add Docker Repository
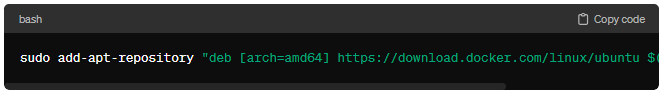
Now, add the Docker repository to your system’s software sources list:
sudo add-apt-repository “deb [arch=amd64] https://download.docker.com/linux/ubuntu $(lsb_release -cs) stable”
Step 5: Install Docker Engine
Once the repository is added, update the package database again:
sudo apt update
Then, install Docker by running:
sudo apt install docker-ce
Step 6: Verify Docker Installation
After the installation is complete, you can verify that Docker is installed correctly by running the following command:
sudo docker –version
This command should output the installed version of Docker, confirming that the installation was successful.
Step 7: Start and Enable Docker Service (Optional)
Docker should start automatically after installation. However, if it’s not running, you can start the Docker service and enable it to start on boot by running the following commands:
sudo systemctl start docker
sudo systemctl enable docker
Step 8: Test Docker Installation
To verify that Docker is working correctly, you can run the “hello-world” container:
sudo docker run hello-world
If Docker is configured correctly, you’ll see a message indicating that your installation is working.
Conclusion:
Congratulations! You’ve successfully installed Docker on your Ubuntu Linux system. Now you can start containerizing your applications and leveraging the power of Docker for development and deployment. If you encounter any issues during the installation process, refer to the Docker documentation or community forums for assistance. Happy containerizing!
How To Install Docker on Ubuntu (F.A.Q)
Is Docker available in Ubuntu's default repositories?
Docker is not available in Ubuntu’s default repositories. Instead, you need to add the Docker repository to your system’s software sources list and install it from there. This ensures that you get the latest version of Docker.
Can I install Docker on older versions of Ubuntu?
While Docker officially supports various versions of Ubuntu, it’s recommended to install Docker on Ubuntu 18.04 LTS or later versions for better compatibility and support. However, if you’re using an older version, you can still install Docker by following the appropriate instructions provided by Docker.
Do I need to have root/sudo privileges to install Docker?
Yes, you need root or sudo privileges to install Docker on Ubuntu Linux. This is because the installation process involves adding repositories, installing packages, and starting system services, which require administrative permissions.