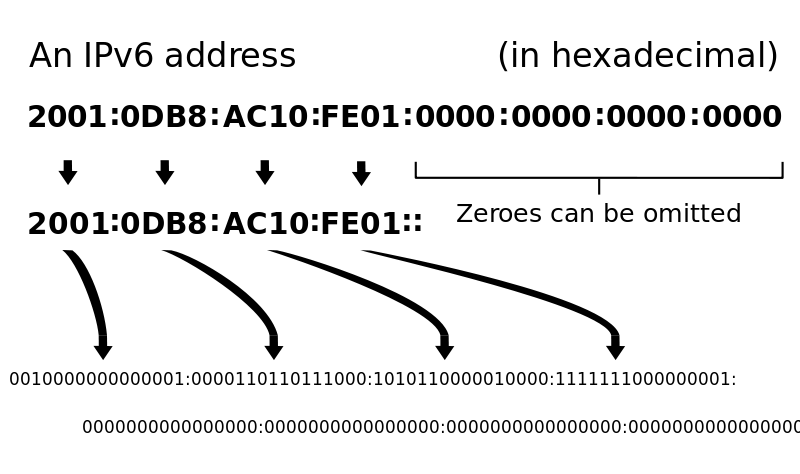An Internet Protocol address is a numerical label such as 197.8.5.1. This address is connected to a computer network that uses the Internet Protocol for communication. An IP address serves two main functions. Network interface identification and location addressing. Internet Protocol version 4 (IPv4) defines an IP address as a 32-bit number. However, because of the growth of the Internet and the depletion of available IPv4 addresses. A new version of IP (IPv6), using 128 bits for the IP address, was standardized in 1998. In contrast, IPv6 deployment has been ongoing since the mid-2000s. IP addresses are written and displayed in human-readable formats, such as 197.8.5.1 in IPv4, and 2001:db8:0:1234:0:567:8:1 in IPv6.
The IP address space is managed globally by the Internet Assigned Numbers Authority (IANA), and by five regional Internet registries (RIRs) responsible in their designated territories for assignment to local Internet registries, such as Internet service providers (ISPs), and other end users. IPv4 addresses were distributed by IANA to the regional internet registry in blocks of approximately 16.8 million addresses each, but have been exhausted at the IANA level since 2011. Only one of the RIRs still has inventory for local operations in Africa. Some Internet Protocol version 4 addresses are reserved for private networks and are not globally unique. A network administrator assigns IP addresses to every device connected to the network. Such assignments can be static (fixed or permanent) or dynamic, depending on network practices and software capabilities.
IPv4 Format And Features
This is the format used to store IPv4 addresses, let’s see its features.
- Millions of devices already support this protocol.
- You can create a basic virtual communication layer between different devices.
- A protocol without connections.
- Addresses are easier to remember and require less storage space.
- Provides conferencing and video library. Provides 12 header fields.
- IPv4 has a checksum field.
IPv6 Format And Features
This is the format used to store IPv6 addresses, let’s see its features.
- Quality of Service (QoS) support
- Hierarchical addressing and routing infrastructure.
- An ideal protocol for neighboring node interactions.
- Stateful and stateless configurations.
- Allow devices to have unique addresses.
- IPv6 address encoding uses a CIDR-like hierarchy, which simplifies routing.
Choosing The Best Internet Protocol Version
As you have seen the features, let’s dive into a quick comparison for choosing the best version.
Performance
The performance of the Internet Protocol version depends on its address size. IPv4 has a 32-bit address space whereas, IPv6 has a 128-bit hexadecimal address space. Furthermore, IPv6 has a larger address space that allows for simpler headers and simplified routing to handle very large address requirements.
Format
IPv6 addresses have four times as many extension headers compared to IPv4 addresses. This additional feature of IPv6 addresses reduces packet processing overhead and header bandwidth, significantly speeding up connections.
Security
When it comes to network security in IPv6, IPSec is mandatory for operation, but optional or paid for in IPv4. In conclusion, this feature of IPv6 helps improve data consistency, network security, and confidentiality.
Faster Speed
IPv6 is faster than IPv4 on network devices because there is no network address translation (NAT). We recommend using IPv6 if high speed is required for network processing.
Conclusion
Lastly, with the comparisons and features known, IPv6 is the winner. But currently, it is used by less number of devices compared to IPv4. Ipv6 addresses are better for working with cloud applications having much faster and more secure data transfer. Besides, IPv4 and IPv6 are inherently incompatible. An intermediate technology is required to ensure compatibility and functionality between the two protocols. IPv4 dominates the Internet space today and is commonly used for hosting server clusters and dedicated servers.
Get Your Own Dedicated Server With IPv4 & IPv6 Support Today