How to Install GUI on CentOS: A Step-by-Step Guide
CentOS is a powerful, community-supported Linux distribution derived from the sources of Red Hat Enterprise Linux (RHEL). While it’s often used as a server OS, some users may prefer to install a graphical user interface (GUI) for easier management. This guide will walk you through the steps to install a GUI on CentOS.
Why Install a GUI on CentOS?
Installing a GUI on CentOS can simplify system management, especially for users who are more comfortable with graphical interfaces than command-line interfaces. It can be particularly useful for tasks such as file management, system monitoring, and running desktop applications.
Prerequisites
Before starting the installation, ensure you have:
- A running instance of CentOS.
- Root or sudo access to the CentOS system.
- A stable internet connection.
Step-by-Step Installation Guide
Step 1: Update the System
First, update your CentOS system to ensure all existing packages are up to date. Open a terminal and run:
sudo yum update -y
Step 2: Install the GUI Packages
CentOS offers several desktop environments, such as GNOME, KDE, and Xfce. This guide will focus on installing GNOME, the default desktop environment for CentOS 7 and CentOS 8.
To install GNOME, run the following command:
sudo yum groupinstall "GNOME Desktop" -y

This command installs all the necessary packages for the GNOME desktop environment.
Step 3: Set the Default Target to Graphical
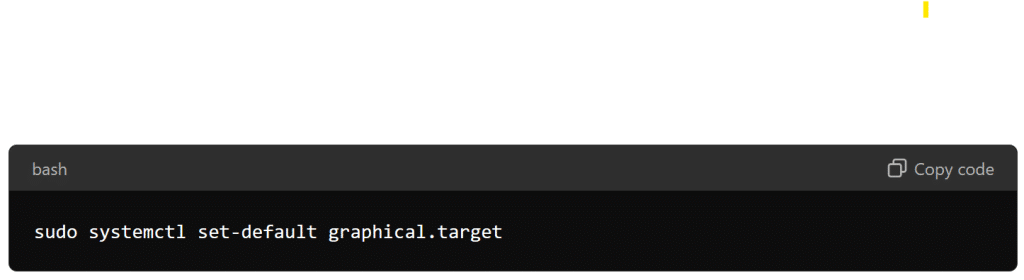
After installing the GUI packages, you need to set the default system target to graphical. The default target determines the mode the system boots into. To set the graphical target as default, run:
sudo systemctl set-default graphical.target
Step 4: Reboot the System
Now, reboot your system to apply the changes and start the graphical interface:
sudo reboot

Step 5: Verify the GUI Installation
Once the system restarts, you should see the GNOME login screen. Log in with your user credentials to access the GNOME desktop environment.
Alternative: Installing Other Desktop Environments
While GNOME is a popular choice, you might prefer other desktop environments like KDE or Xfce. Here’s how to install them:
KDE Plasma
To install KDE Plasma, use the following command:
sudo yum groupinstall "KDE Plasma Workspaces" -y

After installation, set the graphical target and reboot the system as described in the previous steps.
Xfce
To install Xfce, use this command:
sudo yum groupinstall "Xfce" -y

Again, set the graphical target and reboot your system.
Switching Between Desktop Environments
If you have multiple desktop environments installed, you can switch between them at the login screen. Typically, there will be a session menu where you can select the desired desktop environment before logging in.
Conclusion
Installing a GUI on CentOS can make system management more intuitive for users who prefer graphical interfaces. With a few simple commands, you can set up and switch between different desktop environments. Whether you choose GNOME, KDE, or Xfce, having a GUI can enhance your CentOS experience and improve productivity.
Enjoy your new CentOS GUI!
By following these steps, you should be able to install and configure a graphical user interface on your CentOS system with ease. If you encounter any issues or have further questions, feel free to leave a comment below!
How to Install GUI on CentOS (F.A.Q)
Can I install multiple desktop environments on CentOS?
Yes, you can install multiple desktop environments on CentOS. For instance, you can have GNOME, KDE, and Xfce all installed on the same system. At the login screen, you can choose which desktop environment to use for your session.
How do I switch back to the command-line interface (CLI) from the GUI?
If you need to switch back to the command-line interface (CLI), you can change the default target to multi-user, which is the non-GUI target. Run the following command:
sudo systemctl set-default multi-user.target
sudo reboot
This will boot your system into CLI mode. To return to the GUI, set the default target back to graphical:
sudo systemctl set-default graphical.target
sudo rebootHow can I uninstall the GUI from CentOS?
If you decide you no longer need the GUI, you can uninstall it to free up resources. For GNOME, you can use the following command:
sudo yum groupremove "GNOME Desktop"
For KDE Plasma:
sudo yum groupremove "KDE Plasma Workspaces"
For Xfce:
sudo yum groupremove "Xfce"
After uninstalling, you should set the default target to multi-user to ensure the system boots into CLI mode:
sudo systemctl set-default multi-user.target
sudo reboot